Flanges & Weld Fitting
Welding is a process that entails the application of high temperatures, pressure, and sometimes filler material to join two separate components. Contractors can use this procedure to secure piping assemblies, fix heat exchangers, and complete other repairs and installation tasks. In particular, flanges are usually welded or thread-screwed together to form a piping system and effectively attach pumps, valves, pipes, and other parts.
Machine Specialty & Manufacturing is the industry’s leading manufacturer and repair facility for high-pressure flanges, fittings, and custom equipment. We produce exceptional products that adhere to all regulatory requirements and significantly reduce installation, operation, and maintenance time and cost.
Definition of Flanges & Weld Fitting
A flange is a protruding ridge or rim used to increase strength or distribute the load among components. They are commonly found in machines, valves, and specialty applications. Flanges also enable simple washing, inspection, and modification. On the other hand, welded pipe fittings are the joining components that allow valves, pipes, and equipment to be assembled into the pipeline system. They work in conjunction with pipe flanges to allow for flow direction changes.
Flanges and welded pipe fittings come in various materials and grades. However, the most frequently used ones in industrial applications are carbon steel, high-yield carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, duplex and super duplex, and various nickel grades.
Types of Flanges for Pipe Fittings
Flanges are excellent alternatives to welding connections in the piping industry because they can be easily disassembled and maintained. They also come in various designs to accommodate the particular usage and joint strength required.
Identifying a suitable flange design is crucial to achieving strong connectivity, long service life, and optimal pricing. Here are seven common types of flanges used in the piping industry:
Threaded Flanges
Threaded flanges are the most basic type, which is connected by screwing the pipe onto the flange without welding. Still, welding may occasionally be carried out simultaneously with the threaded connection to ensure a stronger attachment. They are also inexpensive and suitable for small-diameter piping systems. Finally, threaded flanges are required in high-explosive environments where welding is risky.
Slip-On Flanges
Slip-on flanges are the most commonly used type in liquid pipelines and are widely available in various sizes. They slip over the connecting pipe as their bore sizes are slightly larger than the pipe’s diameter. They are also attached to the gasket by two welded joints — one inside and one outside the flange cavities.
Socket Weld Flanges
Socket weld flanges have a single welded joint on the flange’s outer side that connects it to the pipe, giving it greater fatigue strength. After the weld, the pipe is inserted into the socket with a small gap to maintain proper pipe positioning. They are suitable for non-corrosive liquid transport in low and high-pressure piping systems.
Lap Joint Flanges
Although largely similar to slip-on flanges, lap joint flanges differ in the radius at the bore intersection and the face to accommodate the stub end. Moreover, they can provide cost-effective mechanical connections while lowering overall piping system costs because they are typically made of lower-quality materials than stubs.
Blind Flanges
Blind flanges are used in pipelines to seal a pipe, valve, or pressure vessel. They are manufactured without a bore and provide an excellent seal even in high-temperature conditions when perfectly merged with the appropriate gaskets.
Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges are distinguished by a long tapered hub welded directly to the connecting pipe. They reduce turbulence and erosion and ensure smooth flow because they are machined to match the inside diameter of the line. Moreover, they are suitable for high or low temperatures, high-pressure conditions, and piping systems with repeated bending.
Special Flanges
Special flanges include loose flanges, high hub blinds, orifice, nipa, expander flanges, and many other customized and specialized flanges for specific uses and applications.
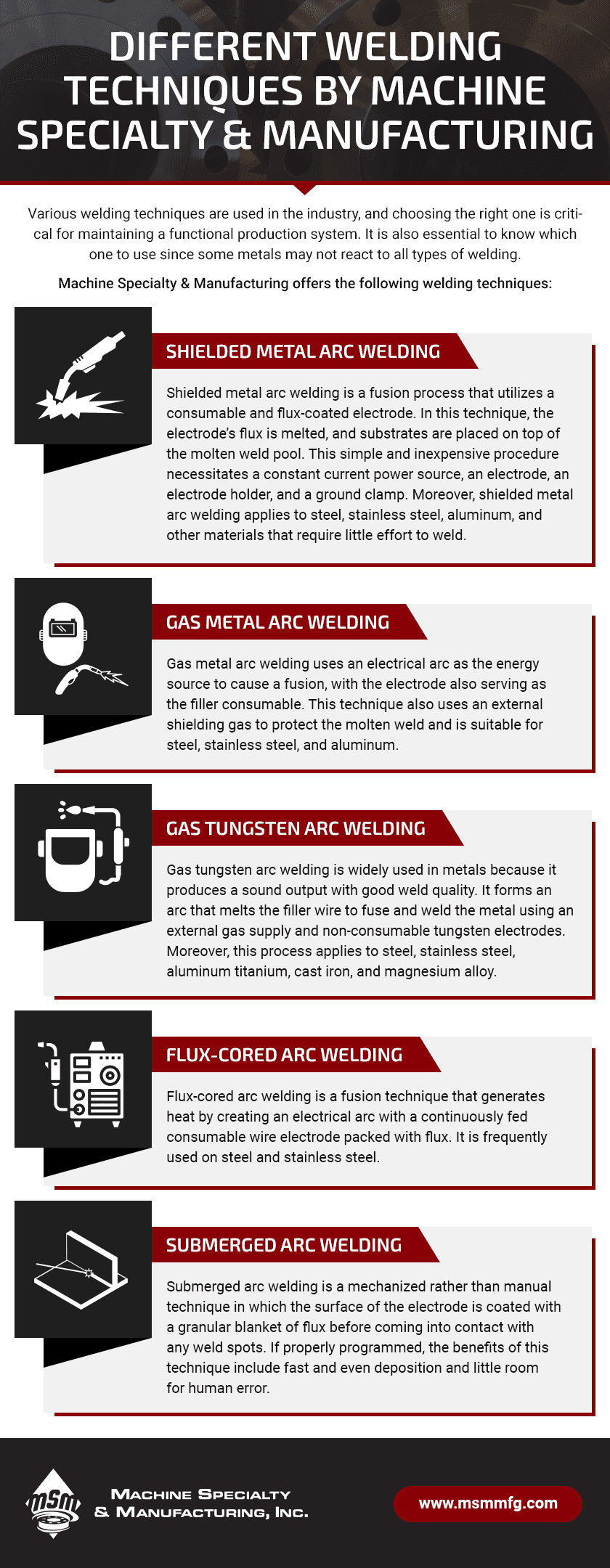
Different Welding Techniques by Machine Specialty & Manufacturing
Various welding techniques are used in the industry, and choosing the right one is critical for maintaining a functional production system. It is also essential to know which one to use since some metals may not react to all types of welding.
Machine Specialty & Manufacturing offers the following welding techniques:
Shielded Metal Arc Welding
Shielded metal arc welding is a fusion process that utilizes a consumable and flux-coated electrode. In this technique, the electrode’s flux is melted, and substrates are placed on top of the molten weld pool. This simple and inexpensive procedure necessitates a constant current power source, an electrode, an electrode holder, and a ground clamp. Moreover, shielded metal arc welding applies to steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and other materials that require little effort to weld.
Gas Metal Arc Welding
Gas metal arc welding uses an electrical arc as the energy source to cause a fusion, with the electrode also serving as the filler consumable. This technique also uses an external shielding gas to protect the molten weld and is suitable for steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
Gas tungsten arc welding is widely used in metals because it produces a sound output with good weld quality. It forms an arc that melts the filler wire to fuse and weld the metal using an external gas supply and non-consumable tungsten electrodes. Moreover, this process applies to steel, stainless steel, aluminum titanium, cast iron, and magnesium alloy.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding
Flux-cored arc welding is a fusion technique that generates heat by creating an electrical arc with a continuously fed consumable wire electrode packed with flux. It is frequently used on steel and stainless steel.
Submerged Arc Welding
Submerged arc welding is a mechanized rather than manual technique in which the surface of the electrode is coated with a granular blanket of flux before coming into contact with any weld spots. If properly programmed, the benefits of this technique include fast and even deposition and little room for human error.
Importance of Hiring a Professional Welding Company
Welding is a potentially hazardous task that most do-it-yourselfers and inexperienced welders are incapable of completing. It also requires specialized pieces of equipment that are not easily accessible. Therefore, hiring professional welding services is crucial.
Here are some other benefits of selecting a professional welding contractor:
Knowledgeable Employees
Trained and experienced welding professionals have access to the instructional materials and understand how to complete tasks correctly and efficiently. Furthermore, companies usually provide their employees with training and seminar sessions to keep them up to date on advanced welding techniques and equipment.
Guaranteed Experience
Most certified companies employ skilled welding inspectors and supervisors. For guaranteed quality services, ensure that these individuals have completed a welding course and have at least five years of work experience before hiring.
Modern Welding Tools
Modern welding tools are available at certified welding companies, allowing experts to provide quality services. In addition, providing the necessary assistance when working with these skilled welders will also be simple.
Liability Insurance
Finally, when looking for a welding company, look for one that is insured. The company will pay for all damages under its insurance policy if something goes wrong.
Need High-Quality Welding Services? Partner With MSM Now!
At Machine Specialty & Manufacturing, we specialize in delivering exceptional weld repairs and fabrication to our customers! We also have tried-and-tested procedures and experienced welders that adhere to ASME and API industry standards, ensuring high-quality products for every requirement.
Get in touch with us today by dialing 1-800-256-1292. You can also request a quote and let MSM find you the best welding services solutions!